Difference between revisions of "TinyOS 1.x Installation on Windows XP"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
* In Cygwin: | * In Cygwin: | ||
** cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF | ** cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF | ||
| − | ** make telosb install.1 bsl, | + | ** make telosb install.1 bsl,0 |
| − | + | ||
| + | * Here is correct output using the MicaZ platform: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Mobilab@herd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF | Mobilab@herd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 22 September 2008
This is a tutorial on how to install TinyOS 1.x on your Windows XP or Vista PC. It assumes you are starting with a clean installation of the OS.
Contents
Configuring the Environment
TinyOS requires Cygwin and a Java development environment. Follow these steps to set this up.
- Download and install Cygwin. Be sure to select cvs, gcc, gdb, openssh, perl, rpm, and vim for installation.
- You may want to add "set nocompatible" to ~/.vimrc to allow insert mode in vim.
- Download and install Sun's latest JDK.
- Download and install Sun's javax.comm package.
- Unzip javacomm20-win32.zip
- Copy win32comm.dll to C:\Program Files\Java\jdkxxxx\jre\bin
- Copy comm.jar to C:\Program Files\Java\jdkxxxx\jre\lib\ext
- Copy javax.comm.properties to C:\Program Files\Java\jdkxxxx\jre\lib
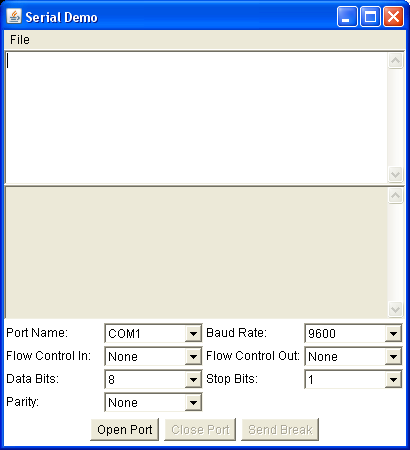
- To test the installation of javacomm, you can run the SerialDemo that is included with the javacomm zip package. It is located in commapi\samples\SerialDemo. If everything is working, you should see the following GUI:
- Download and install graphviz.
- Download and install Eclipse, a Java IDE.
- Download and install a text editor. I recommend Textpad.
Installing TinyOS
The following instructions will download the CVS version of TinyOS. While this may contain some non-stable code, it will give you the most recent version. By checking it out from CVS, you can always switch versions of TinyOS or stay synchronized with the most recent code.
- Download the following RPMs into a temporary folder. They were obtained from here and here:
- If you are using Windows Vista, always start Cygwin in administrator mode.
- In Cygwin, go to the temporary folder with the RPMs and install them using:
- rpm --ignoreos -ivh *.rpm
- In Cygwin, use CVS to download the TinyOS source files.
- Non-Developer access (Note: the second command will prompt for a password, just hit enter):
- cd /opt
- cvs -d:pserver:anonymous@tinyos.cvs.sourceforge.net:/cvsroot/tinyos login
- cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anonymous@tinyos.cvs.sourceforge.net:/cvsroot/tinyos co -P tinyos-1.x
- Developer access: Be sure to configure the shared SSH keys!
- cd /opt
- export CVS_RSH=ssh
- cvs -z3 -d:ext:developername@tinyos.cvs.sourceforge.net:/cvsroot/tinyos co -P tinyos-1.x
- Non-Developer access (Note: the second command will prompt for a password, just hit enter):
- Create file /opt/tinyos-1.x/tools/make/MakeLocal. Here is an example of what it should contain.
- Save washu.sh and tinyos.sh in /etc/profile.d.
- You may have to create /usr/local/bin/locate-jre with the following contents.
- Compile the Java code.
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/tools/java
- make
- Setup java's JNI library:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/tools/java/jni
- make install
Installing Platform Support
TinyOS works on several hardware architectures. Here are instructions on how to add support for Mica2 and TelosB motes.
AVR Tools for Mica/Mica2/MicaZ Motes
- Download the following rpms into a temporary folder:
- Open cygwin and go to the temporary folder that you saved the rpms into and install them using:
- rpm --ignoreos -ivh *.rpm
- If you borrow an IOGear USB-to-Serial cable from the Mobilab (which is silver in color), here are the drivers. If you borrow a black USB-to-serial cable, here are the drivers.
MSP430 Tools for Telos Support
- If you are using TelosB motes, you may download the USB-to-Serial drivers here.
- Download the following rpms into a temporary folder:
- Open cygwin and go to the temporary folder that you saved the rpms into and install them using:
- rpm --ignoreos --nodeps -ivh *.rpm
Installing a TinyOS 1.x Application
We will now verify your TinyOS running the Oscilloscope application that comes with TinyOS 1.x. This application consists of two NesC programs (OscilloscopeRF and TOSBase) and two Java programs (SerialForwarder and oscilloscope). OscilloscopeRF periodically takes a sensor reading and broadcasts it wirelessly. TOSBase forwards the data to the base station. SerialForwarder receives the data from a serial port and forwards it to a local TCP port. Oscilloscope takes the data from the TCP port and displays in a GUI.
Customizing OscilloscopeRF
Before installing the application, you need to go into the source code of OscilloscopeRF to customize which sensor it uses and how frequently it takes a sensor reading. To do this, perform the following operations in Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF
- Open Oscilloscope.nc and change "DemoSensorC" to "Photo" on line 46. This will make it sense light readings.
- Open OscilloscopeM.nc amd change "125" to "8" on line 99. This is the period at which sensor readings will be taken. The period is in binary milliseconds (1024 = 1s). By changing it to 8, we will be taking 128 sensor readings per second.
Compiling and Installing the Application
Now that you have customized OscilloscopeRF, it's time to compile and install it. The following instructions are divided into Mica2 users and TelosB users. Follow the instructions for your platform. After installing the NesC programs, follow the instructions on how to launch the Java applications.
Mica2 users:
- Connect the MIB510 programming board to your computer. Note which serial port it is attached to. To find out, go into Device Manager and see which COM port it shows up as (see picture below). If it is COM1, the corresponding UNIX name is /dev/ttyS0. The UNIX number is always the Windows number - 1. For now, we assume it is attached to /dev/ttyS0.
- Attach a Mica2 mote to the programming board
- In Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF
- make mica2 install.1 mib510,/dev/ttyS4
- Remove the mote from the programming board and attach another mote.
- In Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/TOSBase
- make mica2 install.0 mib510,/dev/ttyS4
- Leave the mote programmed with TOSBase on the programming board.
- Turn on the mote with OscilloscopeRF by plugging in two AA batteries and turning on the switch.
- You should now see the LEDs on both motes blinking.
TelosB users:
- Connect a TelosB mote to your USB port. Note which USB port it shows up as. To find out, go into Device Manager and see which COM port it shows up as. If it is COM1, the corresponding UNIX name is /dev/ttyS0. The UNIX number is always the Windows number - 1. For now, we assume it is attached to /dev/ttyS0.
- In Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF
- make telosb install.1 bsl,0
- Here is correct output using the MicaZ platform:
Mobilab@herd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/OscilloscopeRF
$ make micaz install.1 mib510,/dev/ttyS4
mkdir -p build/micaz
compiling Oscilloscope to a micaz binary
ncc -o build/micaz/main.exe -Os -I../Oscilloscope -DCC2420_DEF_CHANNEL=15 -finli
ne-limit=100000 -Wall -Wshadow -DDEF_TOS_AM_GROUP=0x07 -Wnesc-all -target=micaz
-fnesc-cfile=build/micaz/app.c -board=micasb -I%T/lib/Deluge -DIDENT_PROGRAM_NAM
E=\"Oscilloscope\" -DIDENT_USER_ID=\"Mobilab\" -DIDENT_HOSTNAME=\"herd\" -DIDENT
_USER_HASH=0x3220cae8L -DIDENT_UNIX_TIME=0x47fa71d8L -DIDENT_UID_HASH=0xbbfea11e
L -I/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/CC2420Radio Oscilloscope.nc -lm
/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/platform/micaz/HPLCC2420InterruptM.nc:161: warning: `CCATime
r.start' called asynchronously from `CCA.startWait'
/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/CC2420Radio/CC2420RadioM.nc:116: warning: `Send.sendDone
' called asynchronously from `sendFailed'
compiled Oscilloscope to build/micaz/main.exe
11670 bytes in ROM
493 bytes in RAM
avr-objcopy --output-target=srec build/micaz/main.exe build/micaz/main.srec
avr-objcopy --output-target=ihex build/micaz/main.exe build/micaz/main.ihex
writing TOS image
tos-set-symbols build/micaz/main.srec build/micaz/main.srec.out-1 1
installing micaz binary using mib510
uisp -dprog=mib510 -dserial=/dev/ttyS4 --wr_fuse_h=0xd8 -dpart=ATmega128 --wr_fu
se_e=ff --erase --upload if=build/micaz/main.srec.out-1
Firmware Version: 2.1
Atmel AVR ATmega128 is found.
Uploading: flash
Fuse High Byte set to 0xd8
Fuse Extended Byte set to 0xff
rm -f build/micaz/main.exe.out-1 build/micaz/main.srec.out-1
installing micaz bootloader using mib510
uisp -dprog=mib510 -dserial=/dev/ttyS4 --wr_fuse_h=0xd8 -dpart=ATmega128 --wr_fu
se_e=ff --upload if=/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/Deluge/TOSBoot/build/micaz/main.ihe
x
Firmware Version: 2.1
Atmel AVR ATmega128 is found.
Uploading: flash
Fuse High Byte set to 0xd8
Fuse Extended Byte set to 0xff
- Remove the TelosB mote from your computer and attach another mote.
- In Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/TOSBase
- make telosb install.0 bsl,/dev/ttyS0
- Here is correct output:
Mobilab@herd /opt/tinyos-1.x/apps/TOSBase
$ make micaz install,0 mib510,/dev/ttyS4
mkdir -p build/micaz
compiling TOSBase to a micaz binary
ncc -o build/micaz/main.exe -Os -DCC2420_DEF_CHANNEL=15 -finline-limit=100000 -W
all -Wshadow -DDEF_TOS_AM_GROUP=0x07 -Wnesc-all -target=micaz -fnesc-cfile=build
/micaz/app.c -board=micasb -DTOSH_MAX_TASKS_LOG2=8 -I%T/lib/Deluge -DIDENT_PROGR
AM_NAME=\"TOSBase\" -DIDENT_USER_ID=\"Mobilab\" -DIDENT_HOSTNAME=\"herd\" -DIDEN
T_USER_HASH=0x3220cae8L -DIDENT_UNIX_TIME=0x47fa7219L -DIDENT_UID_HASH=0x7c08b7c
bL -I/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/CC2420Radio TOSBase.nc -lm
/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/platform/micaz/HPLCC2420InterruptM.nc:161: warning: `CCATime
r.start' called asynchronously from `CCA.startWait'
/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/CC2420Radio/CC2420RadioM.nc:116: warning: `Send.sendDone
' called asynchronously from `sendFailed'
compiled TOSBase to build/micaz/main.exe
9768 bytes in ROM
1902 bytes in RAM
avr-objcopy --output-target=srec build/micaz/main.exe build/micaz/main.srec
avr-objcopy --output-target=ihex build/micaz/main.exe build/micaz/main.ihex
writing TOS image
tos-set-symbols build/micaz/main.srec build/micaz/main.srec.out-0 0
installing micaz binary using mib510
uisp -dprog=mib510 -dserial=/dev/ttyS4 --wr_fuse_h=0xd8 -dpart=ATmega128 --wr_fu
se_e=ff --erase --upload if=build/micaz/main.srec.out-0
Firmware Version: 2.1
Atmel AVR ATmega128 is found.
Uploading: flash
Fuse High Byte set to 0xd8
Fuse Extended Byte set to 0xff
rm -f build/micaz/main.exe.out-0 build/micaz/main.srec.out-0
installing micaz bootloader using mib510
uisp -dprog=mib510 -dserial=/dev/ttyS4 --wr_fuse_h=0xd8 -dpart=ATmega128 --wr_fu
se_e=ff --upload if=/opt/tinyos-1.x/tos/lib/Deluge/TOSBoot/build/micaz/main.ihe
x
Firmware Version: 2.1
Atmel AVR ATmega128 is found.
Uploading: flash
Fuse High Byte set to 0xd8
Fuse Extended Byte set to 0xff
- Leave the mote programmed with TOSBase on the programming board.
- Turn on the mote with OscilloscopeRF by plugging in two AA batteries.
- You should now see the LEDs on both motes blinking.
Launching the Java Applications
- In Cygwin:
- cd /opt/tinyos-1.x/tools/java
- java net.tinyos.sf.SerialForwarder &
- java net.tinyos.oscope.oscilloscope
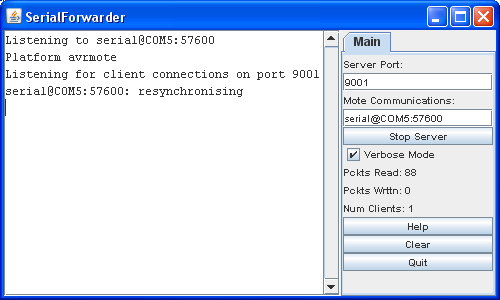
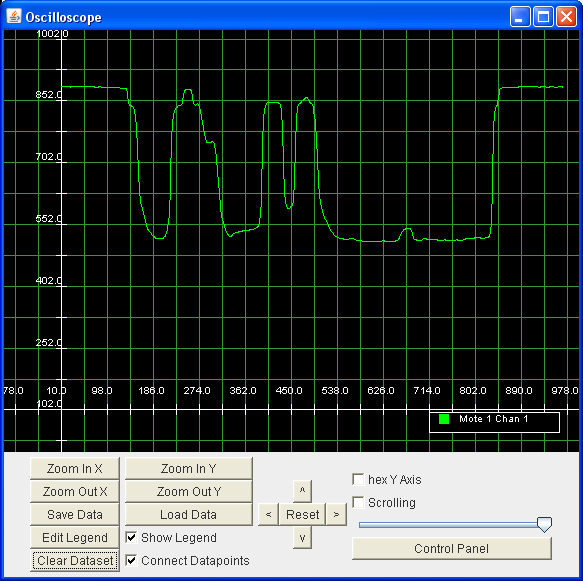
- If everything works, you should see the following:
Possible Errors
Cannot Find javax.comm.Serial
When launching the SerialForwarder, you encounter the following error:
Mobilab@herd /opt/tinyos-1.x/tools/java/jni
$ java net.tinyos.sf.SerialForwarder -comm serial@COM5:57600
Exception in thread "Thread-2" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/comm/Serial
PortEventListener
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(Unknown Source)
at java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.defineClass(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.access$000(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(Unknown Source)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClassInternal(Unknown Source)
at net.tinyos.packet.BuildSource.makeSerial(BuildSource.java:360)
at net.tinyos.packet.BuildSource.makeArgsSerial(BuildSource.java:349)
at net.tinyos.packet.BuildSource.makePacketSource(BuildSource.java:147)
at net.tinyos.packet.BuildSource.makePhoenix(BuildSource.java:87)
at net.tinyos.sf.SFListen.run(SFListen.java:83)
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: javax.comm.SerialPortEventListener
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(Unknown Source)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClassInternal(Unknown Source)
... 17 more
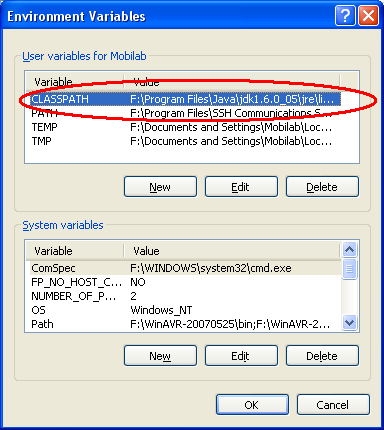
The files that are missing are contained in comm.jar, which should be located in C:\Program Files\Java\jdkxxxx\jre\lib\ext. Ensure that this file is in the CLASSPATH.
- echo $CLASSPATH
If it is not, add it by going into Windows' System Properties.
Also, ensure that you are using the correct version of Java. Type "which java" in Cygwin and ensure that you see the correct JDK:
Mobilab@herd ~ $ which java /cygdrive/f/Program Files/Java/jdk1.6.0_05/bin/java
Note that on many Windows systems, the built-in java is located first in the path, resulting in:
Mobilab@herd ~ $ which java /cygdrive/f/WINDOWS/system32/java
This is not correct and will result in the serial ports not being seen! Be sure the path to the correct jdk is located first in the path!
Invalid Message Size
If you are getting an invalid message size and are using Telos, you may need to include a platforms.properties file in the directory that you are launching Java. Here is an example that sets 'telos' to be the default platform:
##Initial properties for the known platforms #This property file is used to associate the platforms specified in the comm #ID string (e.g. serial@COM1:mica) with various plaftorm-specific parameters #The entry format is as follows: # <platform>=<platform package>, <integer ID>, <baudrate> # where #<platform> -- that's the platform we compile for (i.e. valid nesc target #<platform package> -- name of the common package family that uses the same AM format (e.g. avrmote) #<integer ID> -- unique integer that is used by serial forwarder to identify the platform across the network #<baudrate> -- default serial port datarate used to communicate with the mote #Thu Nov 04 18:44:39 PST 2004 telos=telos,1,57600 tmote=tmote,1,57600 mica=avrmote,2,19200 eyes=eyes,4,19200 micaz=micaz,3,57600 mica2=avrmote,2,57600 mica2dot=avrmote,2,19200