Difference between revisions of "Building Automation"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
* [https://www.auto.tuwien.ac.at/downloads/knxsci06/reinisch-wireless-knxsci06-website.pdf Wireless Communication in KNX/EIB] | * [https://www.auto.tuwien.ac.at/downloads/knxsci06/reinisch-wireless-knxsci06-website.pdf Wireless Communication in KNX/EIB] | ||
* [http://www.bfrl.nist.gov/863/heat_transfer_group/pubs/BFRLSeminar_Dec2005.pdf Wireless Sensor Networks for Applications In and Around Buildings] | * [http://www.bfrl.nist.gov/863/heat_transfer_group/pubs/BFRLSeminar_Dec2005.pdf Wireless Sensor Networks for Applications In and Around Buildings] | ||
| + | * [https://www.rdb.ethz.ch/projects/project.php?proj_id=17833 ETH Building Automation Project] | ||
Revision as of 03:00, 5 May 2008
Building automation was identified, a few years ago, as an effective way of achieving (a) efficient long-term building management and (b) considerable reductions in building energy costs. Some already installed building automation systems (BAS) have successfully achieved between 20% to 80% reductions in energy cost, increased occupant security/safety, increased occupant comfort and a reduction in building operations cost. Although several BAS have been installed so far, they have not yet achieved significant market penetration nor have they been utilized to their full potential. This is due to the existence of several unresolved issues like:
- interoperability between individual sub-systems like HVAC control, lighting control etc.
- use of wireless sensors that facilitate reduced installation/wiring cost
- increased information sharing between the various sub-systems
- integration with installed IT enterprise networks
- better application modeling and deployment toolkits
- increased system reliability
- better algorithms and optimization techniques
- real time monitoring and analysis
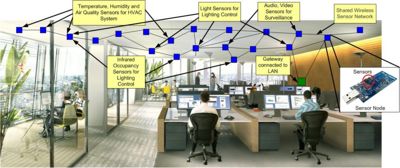
We try to address some of these issues by exploring the feasibility of using WSNs for building automation. The use of wireless sensor networks for building automation enables high-density sensing and control at lower operational costs and could therefore enable more efficient building management. The figure, above, shows an example of a WSN deployment for building automation.
Contents
Sensors
Resources
- NIST Project, Development of testbed for wireless sensor network use in buildings
- DOE report, Advanced Sensors and Controls for Building Applications: Market Assessment and Potential R&D Pathways
- Sensor Networks for Building Automation: Energy Efficiency
- Interesting List of Data Sources
- Österlind, Fredrik and Pramsten, Erik and Roberthson, Daniel and Eriksson, Joakim and Finne, Niclas and Voigt, Thiemo (2007) Integrating Building Automation Systems and Wireless Sensor Networks. In: 12th IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, 25-28 September 2007, Patras, Greece. Tech-Report
- Christian Reinisch, Wolfgang Kastner, Georg Neugschwandtner, Wolfgang Granzer Wireless Technologies in Home and Building Automation, INDIN'07.
- Wireless Communication in KNX/EIB
- Wireless Sensor Networks for Applications In and Around Buildings
- ETH Building Automation Project
Companies
- Millennial Net
- Ember
- Gridlogic
- Siemens
- Honeywell
- Echelon
- Richards-Zeta
People
This work is being conducted by Sangeeta Bhattacharya, a current PhD student, under the guidance of Dr. Chenyang Lu and Dr. Gruia-Catalin Roman.