Difference between revisions of "Cyber-Physical Co-Design of Wireless Monitoring and Control for Civil Infrastructure"
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
[[CPS Publications|'''(Full list of publications)''']] | [[CPS Publications|'''(Full list of publications)''']] | ||
| − | == | + | == Software == |
* Damage Localization Application using DLAC (Washington University) | * Damage Localization Application using DLAC (Washington University) | ||
** [[media:ws2_2008-11-20.zip|Source Code]] | ** [[media:ws2_2008-11-20.zip|Source Code]] | ||
Revision as of 17:16, 20 November 2012
Supported by NSF under the CPS Program
Project Description
The objective of this research is to develop advanced distributed monitoring and control systems for civil infrastructure. The approach uses a cyber-physical co-design of wireless sensor-actuator networks and structural monitoring and control algorithms. The unified cyber-physical system architecture and abstractions employ reusable middleware services to develop hierarchical structural monitoring and control systems.
- The intellectual merit of this multi-disciplinary research includes:
- A unified middleware architecture and abstractions for hierarchical sensing and control;
- A reusable middleware service library for hierarchical structural monitoring and control;
- Customizable time synchronization and synchronized sensing routines;
- A holistic energy management scheme that maps structural monitoring and control onto a distributed wireless sensor-actuator architecture;
- Dynamic sensor and actuator activation strategies to optimize for the requirements of monitoring, computing, and control;
- Deployment and empirical validation of structural health monitoring and control systems on representative lab structures and in-service multi-span bridges.
While the system constitutes a case study, it will enable the development of general principles that would be applicable to a broad range of engineering cyber-physical systems.
This research will result in a reduction in the lifecycle costs and risks related to our civil infrastructure. The multi-disciplinary team will disseminate results throughout the international research community through open-source software and sensor board hardware. Education and outreach activities will be held in conjunction with the Asia-Pacific Summer School in Smart Structures Technology jointly hosted by the US, Japan, China, and Korea.
Team
- Faculty
- Chenyang Lu (Washington University)
- Gul Agha, Bill Spencer (UIUC)
- Shirley Dyke (Purdue University)
- Members
- Greg Hackmann, Bo Li (Washington University)
- Kirill Mechitov, Parya Moinzadeh, Lauren Linderman (UIUC)
- Nestor Castaneda, Sriram Krishnan, Zhuoxiong Sun (Purdue University)
Ongoing Efforts
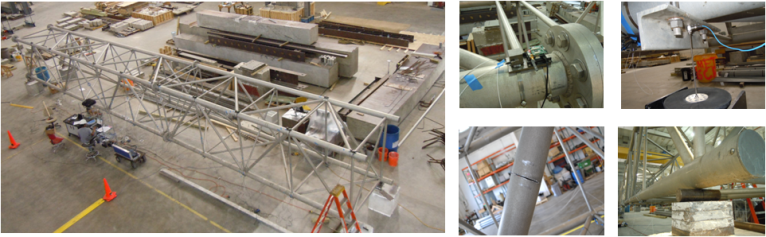
- Full Scale Truss Experiment
- Wireless sensors running distributed, multi-level damage detection deployed on a full scale truss (17.04m L × 1.83m W × 1.98m H) at Purdue;
- Damage detection results reflect actual damage locations, matching results from simulation.
- Jindo Bridge Monitoring
- Field validation of wireless sensor-based monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge in Korea;
- Long-term autonomous monitoring using 113 wireless smart sensors;
- Establishment of an international testbed.
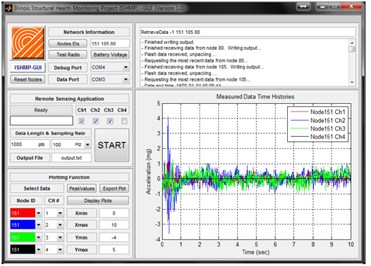
- Monitoring Services Toolsuite
- Modular, service-oriented software library for assembling scalable monitoring applications;
- Core services: universal sensing, time synchronization, reliable communication, multi-hop routing, power management, numerical library;
- Used by 75 groups in 15 countries.
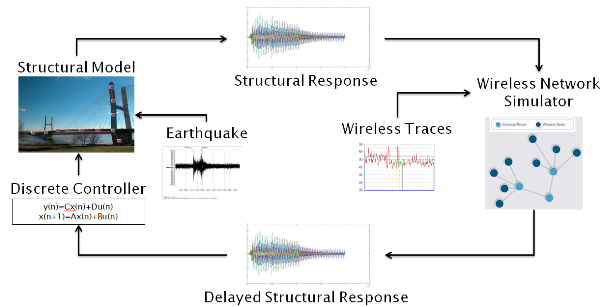
- Structural Control Simulator
- A cyber-physical simulation framework combining state-of-the-art structural models and wireless networking simulation;
- Enables realistic design and testing of structural control systems based on WSANs.
Publications
Software
- Damage Localization Application using DLAC (Washington University)
- Illinois SHM Services Toolsuite
- Prof. Chenyang Lu, Real-Time Wireless Control Networks: Challenges and Directions, The NITRD National Workshop on The New Clockwork for Time-Critical Systems, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, October 25-27, 2012.
- Prof. Chenyang Lu, Cyber-Physical Co-Design for Wireless Structural Health Monitoring, Distinguished Lecture, University of Louisville, Nov. 2011.
- Prof. Chenyang Lu, My (biased) Perspective on CPS, Panel on Networked Monitoring and Control/Cyber-Physical Systems, Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems (ECRTS'11), Porto, Portugal, July 2011.
- Hackmann, G., "Cyber-Physical Codesign of Distributed Structural Health Monitoring With Wireless Sensor Networks", ICCPS 2010 presentation, April 13, 2010. [PPTX] [PDF]
- Prof. Chenyang Lu, Distributed Structural Health Monitoring, CONet Joint Seminar, Swedish Institute of Computer Science (SICS), Stockholm, Sweden, July 2009.
- Hackmann, G., "A Holistic Approach to Decentralized Structural Damage Localization Using Wireless Sensor Networks", RTSS 2008 presentation, December 1, 2008. [PPTX] [PDF]