Building Automation
Building automation was identified, a few years ago, as a major means of reducing energy usage in buildings. Some already installed building automation systems (BAS) have achieved between 20\% to 80\% reductions in energy cost, increased occupant security/safety, increased occupant comfort and a reduction in building operations cost. Although several building automation systems (BAS) have been installed so far, they have not yet achieved a significant market penetration nor have they successfully achieved their full potential. Several issues still remain unresolved, like:
- increased interoperability between individual sub-systems like HVAC, lighting control etc.
- use of wireless sensors that facilitate reduced installation/wiring cost
- increased information sharing between the various sub-systems
- integration with installed IT enterprise networks
- better application modeling and deployment toolkit
- real time monitoring and analysis
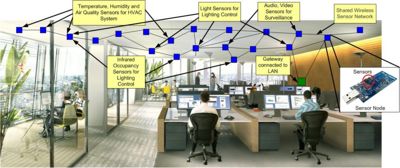
In this project we try to explore the use of WSNs for building automation. The use of sensor networks for building automation enables high-density sensing and control at lower operational costs and could therefore enable more efficient building management. Figure 1. shows an example of a WSN deployment for building automation.
Contents
Sensors
- Air Quality Sensors
- IR/acoustic Sensors
Resources
- NIST Project, Development of testbed for wireless sensor network use in buildings
- DOE report, Advanced Sensors and Controls for Building Applications: Market Assessment and Potential R&D Pathways
- Sensor Networks for Building Automation: Energy Efficiency
- Interesting List of Data Sources
Companies
- Millennial Net
- Ember
- Gridlogic
- Siemens
- Honeywell
People
This work is being conducted by Sangeeta Bhattacharya, a current PhD student, under the guidance of Dr. Chenyang Lu and Dr. Gruia-Catalin Roman.